Plex
This article describes how to download a specific dashboard pack. You can download dashboard packs from dashboards.squaredup.com and learn more about how dashboard packs work here: Dashboard Packs
Description
This Plex dashboard displays statistics from a Plex Media Server (PMS) library without launching the Plex app or webpage. Created using PowerShell tiles that target the Plex’s REST APIs and the PMS server.
How do I import and configure this dashboard?
Ensure you're using SquaredUp DS v5.4 or above.
Already a SquaredUp customer?
Get the latest version of SquaredUp DS Standalone
New to SquaredUp?
- Create a PowerShell profile in SquaredUp DS with the following settings: NamePlex
Note: The name is case-sensitive and must be entered exactly as given here for the tiles to recognize the profile automatically. If you name it differently, you will need to select the profile manually for each tile on the dashboard.
Description (optional)Used to connect to a Plex Media ServerScriptCopy and paste the contents of the PowerShell script below.Note: You will need to change the values for the parameters$lSrvUsername,$lSrvPassword,$lServerIP,$lPlexUsername,$lPlexPassword,$tokenPath, and$ClientGUIDaccording to the description in the script.#------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Credentials for the Server that is Hosting Plex $SrvUsername = $lSrvUsername # Login Credentials to check Services $SrvPassword = $lSrvPassword # Password for credentials $ServerIP = $lServerIP # IP of your Plex Server #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Credentials for Plex $PlexUsername = $lPlexUsername # Your Plex username $PlexPassword = $lPlexPassword # Your Plex password #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Constants $tokenPath = "C:\SquaredUp\PlexToken.txt" # Path and Folder that holds token $ClientGUID = '<insert your own GUID>' # Create your own GUID $Product = 'SquaredUp' # Can be anything $version = '1.00.0.0001' # Can be anything #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Credentials Function function New-Credential([String]$UserName, [SecureString]$Password) { $credentials = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential $Username, $password $credential = Get-Credential -Credential $Credentials $credential } # Process Function function New-Process([String]$name, [String]$state, [DateTime]$startTime, [String]$note) { $obj = New-Object -TypeName psobject $obj | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name Name -Value $name $obj | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name State -Value $state $obj | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name StartTime -Value $startTime $obj | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name Note -Value $note $obj } #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Create credentials $CredServer = New-Credential -UserName $SrvUsername -Password ($SrvPassword | ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText -Force) $CredPlex = New-Credential -UserName $PlexUsername -Password ($PlexPassword | ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText -Force) #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Create Plex Certificate Address by retreiving the CertificateUUID from the Server $CertificateUUID = (Invoke-Command -ComputerName $ServerIP -Credential $CredServer -ScriptBlock { Get-ItemProperty -Path 'HKCU:\Software\Plex, Inc.\Plex Media Server' -Name "CertificateUUID" }).CertificateUUID $PlexServer = "https://" + $ServerIP.Replace(".","-") + "." + $CertificateUUID + ".plex.direct:32400" #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Fetch the saved token from the file system $token = Get-Content -Path $tokenPath #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # API Parameters $headers = @{ 'accept' = 'application/json' } $chkBody = @{ 'accept' = 'application/json' 'X-Plex-Product' = $Product 'X-Plex-Client-Identifier' = $ClientGUID 'X-Plex-Token' = $token } $authheader = @{ 'X-Plex-Client-Identifier' = $ClientGUID 'X-Plex-Product' = $Product 'X-Plex-Version' = $version 'Authorization' = $CredPlex.GetNetworkCredential().UserName 'Accept' = 'application/json' } #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Check if Auth Token is valid Try { $session = Invoke-RestMethod -Method Get -Headers $headers -Body $chkBody -Uri https://plex.tv/api/v2/user $isValid = $true } catch { Write-Host "Authorization token has expired or something else is wrong" $isValid = $false } #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # If the token is invalid, request a new token if ($isValid -eq $false) { Try { $uri = 'https://plex.tv/users/sign_in.json' $session = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $uri -Method Post -Credential $CredPlex -Headers $authheader #Here is our new token $token = $session.user.authentication_token } catch { #Reset token because there was an error $isValid = $true } } #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ #Save the token to the file system, but only if it is different if ($isValid -eq $false) { try { # Attempt to save the new token Set-Content -Path $tokenPath -Value $token } catch { # There was a failure, try one more time but wait a couple of seconds $rnd = Get-Random -Minimum 500 -Maximum 2000 Start-Sleep -Milliseconds $rnd Set-Content -Path $tokenPath -Value $token } } $headers = @{ 'accept' = 'application/json' 'x-Plex-Token' = $token } # Spread the Plex Love! #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Begin Dashboard Tiles- From the top right hand menu ☰ click system.
- Go to the PowerShell tab.
- Click add new profile.
- Enter a name and a description for the new profile.
- Enter the profile script.
- Click add profile.
The profile is now saved and can be used in a PowerShell tile.
For more help creating a PowerShell profile see How to use the PowerShell tile
- Create a Run As account in SquaredUp DS with the following settings: NameDashboardUsername and passwordEnter the credentials you want to use for this Run As account
PowerShell Run As accounts contain the credentials that define the permissions deciding how PowerShell scripts are run (both the script in the tile and the profile script chosen for the tile).
The PowerShell Run As account Default comes with every SquaredUp DS installation and uses the SquaredUp DS app pool identity to run the scripts. Since running PowerShell scripts within the SquaredUp DS application pool process can pose a security risk and affect SquaredUp DS performance, you can change the default Run As to use a different account.
You can also add new Run As accounts to be able to execute scripts with different credentials.
- From the top right hand menu ☰ click system.
- Go to the PowerShell tab.
- In the Run As section, click on the + button to add a new Run As.
- Enter a name and a description for your new Run As.
Note: Once you have saved the Run As account, you can't change its name anymore. You can always change the description. - Enter the user credentials you want to use for this Run As account.
Do not use your own or anyone's personal user account for Run As accounts. Instead, create a new account that is not used by a specific person (a "service account"), but only used for running PowerShell scripts. Consider the permissions of this service account carefully.
Required permissions for service accounts:
The service account you use for Run As must have at least the following permission:
- Allow log on locally
If you don't use the default NetworkService as your application pool identity, you might see the following error message when using Run As accounts: A required privilege is not held by the client.
In this case you need to add the application pool identity to the following policies:
- Adjust memory quotas for a process
- Replace a process-level token (you need to reboot the server for this policy to take effect)
The user credentials you enter for the Run As account are used to run all PowerShell scripts in tiles that use the Run As account. Once created, your Run As account can be used by other SquaredUp DS administrators to run their scripts. By using your or any user's credentials, you lose control over which scripts are executed in the name of this user which can cause privacy issues. In addition to that, users often have more rights than a script would need. By using a user account with extensive permissions, scripts that use the Run As can exploit those permissions.
- Click save to save the new Run As account.
The Run As account is now available in PowerShell tiles and can be used to execute scripts.
1) For all Run As accounts: Use a service account, not a user account for Run As accounts.
Do not use your own or anyone's personal user account for Run As accounts. Instead, create a new account that is not used by a specific person (a "service account"), but only used for running PowerShell scripts. Consider the permissions of this service account carefully.
Required permissions for service accounts:
The service account you use for Run As must have at least the following permission:
- Allow log on locally
If you don't use the default NetworkService as your application pool identity, you might see the following error message when using Run As accounts: A required privilege is not held by the client.
In this case you need to add the application pool identity to the following policies:
- Adjust memory quotas for a process
- Replace a process-level token (you need to reboot the server for this policy to take effect)
The user credentials you enter for the Run As account are used to run all PowerShell scripts in tiles that use the Run As account. Once created, your Run As account can be used by other SquaredUp DS administrators to run their scripts. By using your or any user's credentials, you lose control over which scripts are executed in the name of this user which can cause privacy issues. In addition to that, users often have more rights than a script would need. By using a user account with extensive permissions, scripts that use the Run As can exploit those permissions.
- From the top right hand menu ☰ click system.
- Go to the PowerShell tab.
- In the Run As section, click on the + button to add a new Run As.
- Enter a name and a description for your new Run As.
Note: Once you have saved the Run As account, you can't change its name anymore. You can always change the description. - Enter the user credentials you want to use for this Run As account.
Do not use your own or anyone's personal user account for Run As accounts. Instead, create a new account that is not used by a specific person (a "service account"), but only used for running PowerShell scripts. Consider the permissions of this service account carefully.
Required permissions for service accounts:
The service account you use for Run As must have at least the following permission:
- Allow log on locally
If you don't use the default NetworkService as your application pool identity, you might see the following error message when using Run As accounts: A required privilege is not held by the client.
In this case you need to add the application pool identity to the following policies:
- Adjust memory quotas for a process
- Replace a process-level token (you need to reboot the server for this policy to take effect)
The user credentials you enter for the Run As account are used to run all PowerShell scripts in tiles that use the Run As account. Once created, your Run As account can be used by other SquaredUp DS administrators to run their scripts. By using your or any user's credentials, you lose control over which scripts are executed in the name of this user which can cause privacy issues. In addition to that, users often have more rights than a script would need. By using a user account with extensive permissions, scripts that use the Run As can exploit those permissions.
- Click save to save the new Run As account.
The Run As account is now available in PowerShell tiles and can be used to execute scripts.
2) We strongly recommend you change the Default Run As account to the credentials you want to use as the default Run As.
Every PowerShell tile needs a Run As and if you haven't created a Run As yet, tiles will use the Default Run As. The Default Run As uses the SquaredUp DS app pool to run scripts. The SquaredUp DS app pool account might grant too many permissions that are not needed for your scripts and can potentially damage your system, which is why using this default account is not recommended. Create a service account that you want to use for the Default Run As and change the Default Run As to use those credentials.
- From the top right hand menu ☰ click system.
- Go to the PowerShell tab.
You see the Default Run As. If you haven't changed the Default Run As account yet, you see a yellow icon indicating that the Run As uses the not recommended default setting "run as SquaredUp DS app pool".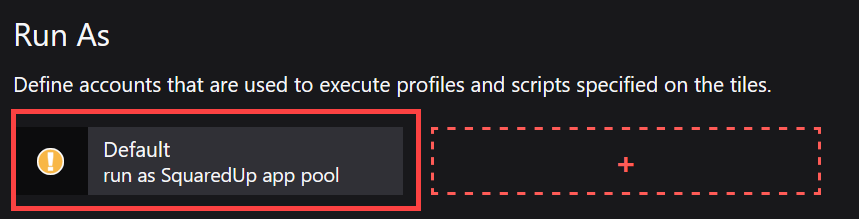
- Click on the Default Run As to edit it.
As long as the Run as SquaredUp DS app pool toggle is on, the Default Run As is read only.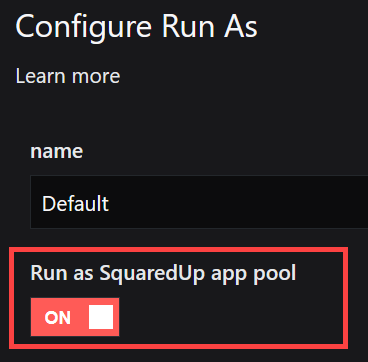
- Switch the Run as SquaredUp DS app pool toggle to off.
- Change the description to indicate that the Default Run As no longer uses the SquaredUp DS app pool.
- Enter the user credentials you want to use for the Default Run As.
Do not use your own or anyone's personal user account for Run As accounts. Instead, create a new account that is not used by a specific person (a "service account"), but only used for running PowerShell scripts. Consider the permissions of this service account carefully.
Required permissions for service accounts:
The service account you use for Run As must have at least the following permission:
- Allow log on locally
If you don't use the default NetworkService as your application pool identity, you might see the following error message when using Run As accounts: A required privilege is not held by the client.
In this case you need to add the application pool identity to the following policies:
- Adjust memory quotas for a process
- Replace a process-level token (you need to reboot the server for this policy to take effect)
The user credentials you enter for the Run As account are used to run all PowerShell scripts in tiles that use the Run As account. Once created, your Run As account can be used by other SquaredUp DS administrators to run their scripts. By using your or any user's credentials, you lose control over which scripts are executed in the name of this user which can cause privacy issues. In addition to that, users often have more rights than a script would need. By using a user account with extensive permissions, scripts that use the Run As can exploit those permissions.
- Click save to save the changes.
The Default Run As profile now uses the user account you entered when executing scripts.
3) Consider disabling the option to use the SquaredUp DS app pool for the Default Run As.
To make sure that the SquaredUp DS app pool can't be used after you changed the Default Run As, you can disable the option to use the SquaredUp DS App pool.
By default, the toggle Run as SquaredUp DS app pool is visible in the Default Run As account. By setting this toggle to on, the Default Run As can be (re)set to use the SquaredUp DS app pool to run scripts. SquaredUp DSadministrators can disable the toggle to prevent that the SquaredUp DSapp pool can be used for running PowerShell scripts.

- If you haven't already done it, change the Default Run As from using the SquaredUp DS app pool to using the credentials you want to use.
Note: If you disable the toggle Run as SquaredUp DS app pool while the Default Run As still uses the SquaredUp DS app pool (toggle on), the credentials in the Default Run As will be empty and any PowerShell tiles using the Default Run As will show an error. You need to go into the Default Run As and enter the credentials you want to use to fix this issue.- From the top right hand menu ☰ click system.
- Go to the PowerShell tab.
You see the Default Run As. If you haven't changed the Default Run As account yet, you see a yellow icon indicating that the Run As uses the not recommended default setting "run as SquaredUp DS app pool".
- Click on the Default Run As to edit it.
As long as the Run as SquaredUp DS app pool toggle is on, the Default Run As is read only.
- Switch the Run as SquaredUp DS app pool toggle to off.
- Change the description to indicate that the Default Run As no longer uses the SquaredUp DS app pool.
- Enter the user credentials you want to use for the Default Run As.
Do not use your own or anyone's personal user account for Run As accounts. Instead, create a new account that is not used by a specific person (a "service account"), but only used for running PowerShell scripts. Consider the permissions of this service account carefully.
Required permissions for service accounts:
The service account you use for Run As must have at least the following permission:
- Allow log on locally
If you don't use the default NetworkService as your application pool identity, you might see the following error message when using Run As accounts: A required privilege is not held by the client.
In this case you need to add the application pool identity to the following policies:
- Adjust memory quotas for a process
- Replace a process-level token (you need to reboot the server for this policy to take effect)
The user credentials you enter for the Run As account are used to run all PowerShell scripts in tiles that use the Run As account. Once created, your Run As account can be used by other SquaredUp DS administrators to run their scripts. By using your or any user's credentials, you lose control over which scripts are executed in the name of this user which can cause privacy issues. In addition to that, users often have more rights than a script would need. By using a user account with extensive permissions, scripts that use the Run As can exploit those permissions.
- Click save to save the changes.
The Default Run As profile now uses the user account you entered when executing scripts.
On the SquaredUp server, run Notepad as administrator (Start, Run, type
notepad, and then right-click and select Run as administrator).In Notepad, open the
security.jsonfile from the SquaredUp DS folder:...\User\Configuration\security.jsonIf the file doesn't exist, create it by following these steps and saving the file as
security.jsonat the end.Name of the SquaredUp folder
The default name of the SquaredUp folder is
SquaredUpfor v6 and above.For v5 it is
SquaredUpv5.Location of the SquaredUp folder
If you deployed SquaredUp DS via the Azure or AWS Marketplace:
The default location for the SquaredUp folder is
F:\.SquaredUpv[Version Number]
For v5 it isF:\SquaredUpv5.If you installed SquaredUp DS using the installer:
A custom location may have been chosen during the installation.
The default location for the SquaredUp folder is
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\SquaredUpFor v5 it is
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\SquaredUpv5.
Edit the JSON file to contain the following property:{ "enable-powershell-run-as-app-pool": false }
If the file already contains settings, then you will need to add a comma at the end of the previous line.- Save the JSON file.
- Recycle the SquaredUp DS application pool.
The toggle Run as SquaredUp DS app pool is now disabled and hidden. It is not possible to (re)set the Default Run As to use the SquaredUp DS app pool anymore.
4) Consider creating different service accounts for running different scripts, depending on what their purpose is and what permissions they need. Save each service account as a different Run As account in SquaredUp DS.
Download and import this dashboard pack.
- Download the dashboard pack zip file for the dashboard pack you wish to import.
There may be additional steps before or after the import to get the dashboard working in your environment.
- In DS Standalone go to the top right hand menu ☰ > Import Dashboard Packs and drag the zip file into the Manual Import box.
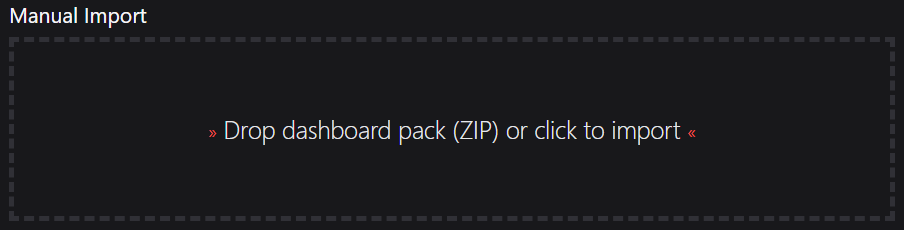
- The dashboard pack is imported and if the pack contains top-level dashboards, these will automatically appear in the navigation bar, usually in a folder called 'Community Dashboards' for dashboard packs from the SquaredUp Community.
- Carry out any additional steps required to make the dashboard work in your environment. These steps will be described on the download page for each dashboard. For example, you may need to create the correctly named Web API provider, create a PowerShell profile, or edit tile scopes.
- Edit the imported dashboard as required.
- Download the dashboard pack zip file for the dashboard pack you wish to import.
- Edit the PowerShell tiles if necessary.
Based on your environment and the fields retrieved by your SQL queries you might need to adapt the script in the PowerShell tiles.- Edit the tiles by clicking the Edit button.
- Open the script panel.
- Edit the script according to your environment.
Publish the dashboard.
A newly created dashboard will not be visible to others until it is published.
Only admins can publish dashboards, unless you have been given author permissions to a Team Folder see Team Folders
If you made changes to an existing dashboard, the changes will only be visible to others after you published the dashboard again.
You can identify a dashboard that has not been published yet or has unpublished changes by the unpublished button at the top:

When you click on the unpublished button, you'll have two options:
- Publish will make the dashboard or changes visible to others.
Note: A newly created dashboard will appear on the menu where you created it. To move the dashboard to a different place on the navigation bar see How to edit the Navigation Bar. - Discard will delete your draft dashboard if it has never been published or, if you made changes to an already published dashboard, discard the changes.
Publishing dashboards to different audiences
Find out how to publish dashboards to a subset of users using Team Folders or visible to anyone even unlicensed users with Open Access (Sharing Dashboards with anyone - Open Access).
- Publish will make the dashboard or changes visible to others.